Sapphire
Sapphire has exceptional physical (optical, mechanical, dielectric and thermal) and chemical properties along with superior radiation stability. For this reason sapphire is in high demand for many Scientific, Industrial and Military applications.
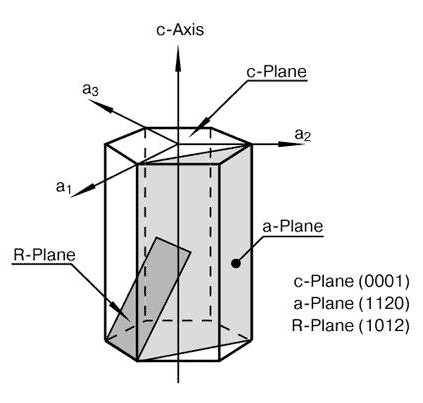
Sapphire has orientations and the following picture shows the structure of the primary planes of the sapphire crystal corresponding to the structure system of sapphire. Shown in this Figure, the C– plane is (0001), A– plane is (1120) and R– plane (1012).
There are many different methods for growing sapphire. The most common are:
Kyropoulos (HEM) method
Stepanov (EFG) method
Czochralski method
Bagdasarov (Horizontal directed crystallization) method
Verneuil method
Sapphire Physical properties
Crystal structure: | |
Chemical composition: | Al2O3 |
Molecular weight: | 101.96 |
Crystal system: | Rhombohedral systems(R3c) |
Lattice constant: | a=4.765A/c=13.001A* |
Density (specific gravity): | 3.98 g/cm3 |
Cleavability: | (1011), (1120), imperfect |
Mechanical properties: | |
Hardness: | [Mohs] 9(*Diamond=10, quartz=7) [Knoop] 15.0 to 16.3GPa (perpendicular to the c axis) 16.4 to 19.6GPa (parallel to the c axis) [Vickers] 2300 |
Young’s modulus: | 34 to 37 GPa |
Crushing strength: | 2000 Mpa |
Tensile strength: | 2250 Mpa |
Compression strength: | 2950 Mpa |
Bending strength: | 450 to 690 Mpa |
Destruction coefficient: | 490 to 690 Mpa |
Bulk modulus of elasticity: | 250 GPa |
Shearing modulus: | 140 Gpa |
Optical Properties | |
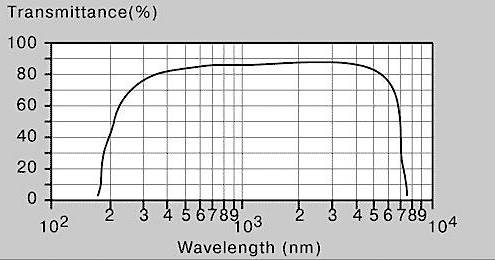
Transmittance: |
|
Refractive index: | 1.83 at 0.26 mm |
JH OPTEK can provide sapphire window, lens, prism, wafer and other customized parts. The coating is available based on customer request as well.